Whether you have a hillside, slope along a waterway or a previously eroded space, native plants can help preserve the soil and maintain the land. Erosion can occur from wind, gravity, water and even over-use. Utilizing native plants can help anchor soil and reduces run-off.
- How do native plants prevent erosion?
- Why are native plants better?
- Why are native plants better than non-native plants?
- What plants are good for erosion?
- What can you plant on a hill to stop erosion?
- How do farmers use plants to slow erosion?
- How can you tell if a plant is native?
- What are two ecological benefits of a native plant garden?
- How do you plan a native plant garden?
- Is it OK to plant non-native plants?
- Can a native plant be invasive?
- Why are non-native plants important?
How do native plants prevent erosion?
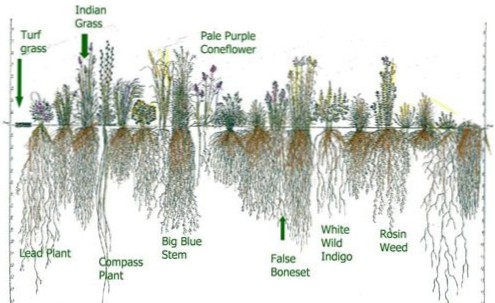
Using native plants for erosion control is an excellent biological method to help protect the landscape from erosive forces. Native grasses and sedges are particularly effective due to their fibrous roots that grab and hold the soil, keeping it from washing away.
Why are native plants better?
Native Gardening
Native plants are also advantageous, because: Native plants do not require fertilizers and require fewer pesticides than lawns. Native plants require less water than lawns and help prevent erosion. The deep root systems of many native Midwestern plants increase the soil's capacity to store water.
Why are native plants better than non-native plants?
Native plants are well adapted to their surroundings, they use less water and need less maintenance than non-native plants and in some cases have natural resistance to pests. ... The Benefits of Native Gardens include saving water, low maintenance requirments, reducing pesticides and creating a habitat for native wildlife.
What plants are good for erosion?
Cover crops, such as vetch, rye and clover, are excellent plants for erosion control. These hardy easy to grow plants send out nets of roots that help hold topsoil in place while also reducing competitive weeds. When tilled back into the soil, they increase the nutrient density as they compost.
What can you plant on a hill to stop erosion?
Here's what you can do to strengthen a hilly landscape:
- Grasses. Ornamental grasses like mondo, blue fescue, and yellow foxtail are ideal erosion fighters. ...
- Ground Covers and Shrubs. Sturdy ground covers and shrubs are a great way to deter foot traffic through an area (another contributor to soil erosion). ...
- Trees.
How do farmers use plants to slow erosion?
Planting Vegetation as ground cover: Farmers plant trees and grass to cover and bind the soil. Plants prevent wind and water erosion by covering the soil and binding the soil with their roots. The best choice of plants to prevent soil erosion are herbs, wild flowers and small trees.
How can you tell if a plant is native?
A plant is considered native if it has occurred naturally in a particular region, ecosystem, or habitat without human introduction. Exotic plants that evolved in other parts of the world or were cultivated by humans into forms that don't exist in nature do not support wildlife as well as native plants.
What are two ecological benefits of a native plant garden?
Because native plants are adapted to local environmental conditions, they require far less water, saving time, money, and perhaps the most valuable natural resource, water. In addition to providing vital habitat for birds, many other species of wildlife benefits as well.
How do you plan a native plant garden?
Consider these fundamentals as you design your native plant garden:
- Match plants to your site. Look at your landscape. ...
- Design for succession of bloom. ...
- Group similar plants together. ...
- Keep your plants in scale. ...
- Define the space. ...
- Control Perennial Weeds.
Is it OK to plant non-native plants?
Invasive plants are always non-native plants. Sometimes, when non-native plants are introduced to a new habitat, they can “take over”, causing a lot of problems for your local ecosystem. This includes negative affects on wildlife, insects, forests, trees, plants… and much more. In short: they are bad news.
Can a native plant be invasive?
Can Native Plants Become Invasive? A native plant can become invasive, even after years of growing it without any problems. ... When they grow out of control, push out other plants, disrupt the local ecosystem, and cause other undesirable changes, we may consider them to have become invasive.
Why are non-native plants important?
Some non-native species provide habitat and food for native animals and plants, for example. In the southwestern United States, tamarisk trees have been aggressively spreading along rivers. ... Introduced species can also help restore native ecosystems on degraded land.
 CorseMachin
CorseMachin



Yet No Comments